IT INFO

양자 역학(Quantum Mechanics)은 현대 물리학의 가장 중요한 분야 중 하나로, 원자 및 아원자 입자 수준에서 물질과 에너지를 설명하는 이론입니다. 고전 물리학으로는 설명할 수 없는 자연 현상을 이해하기 위해 20세기 초에 발전하기 시작했습니다. 양자 역학은 우리의 세계를 이해하는 데에 매우 근본적인 관점을 제공하며, 오늘날 다양한 과학 및 기술 혁신의 기초가 되고 있습니다.
Quantum mechanics is one of the most critical fields of modern physics, describing matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic levels. It began to develop in the early 20th century to explain natural phenomena that classical physics could not. Quantum mechanics provides a fundamental perspective on understanding our world and forms the basis for many scientific and technological innovations today.

양자 역학의 기본 원리
- 양자화(Quantization): 에너지와 다른 물리량은 연속적이지 않고 불연속적인 작은 단위인 양자(quanta)로 나뉩니다. 예를 들어, 전자가 원자 주위를 도는 에너지는 특정 값만 취할 수 있습니다.
- 파동-입자 이중성(Wave-Particle Duality): 물질과 빛은 동시에 입자와 파동의 성질을 지닙니다. 예를 들어, 전자는 입자로 간주되지만, 특정 조건에서 파동처럼 간섭 및 회절 현상을 나타냅니다.
- 불확정성 원리(Uncertainty Principle): 하이젠베르크가 제안한 이 원리는 입자의 위치와 운동량을 동시에 정확히 알 수 없음을 의미합니다. 즉, 한 물리량을 정밀하게 측정할수록 다른 물리량은 더 불확정해집니다.
- 슈뢰딩거 방정식(Schrödinger Equation): 양자 시스템의 상태를 기술하는 방정식으로, 입자의 파동함수를 통해 시간과 공간에서 입자의 상태를 나타냅니다.
- 파동함수의 붕괴(Wavefunction Collapse): 측정을 통해 입자의 상태가 특정 값으로 결정되기 전, 입자는 여러 가능성을 동시에 갖고 있습니다. 이를 '중첩(superposition)' 상태라고 하며, 관측이 이루어지는 순간 특정 상태로 붕괴됩니다.
Fundamental Principles of Quantum Mechanics
- Quantization: Energy and other physical quantities are not continuous but are divided into discrete units called quanta. For example, the energy levels of an electron orbiting an atom can only take on specific values.
- Wave-Particle Duality: Matter and light exhibit both particle-like and wave-like behavior. For instance, electrons are considered particles but can show interference and diffraction patterns under certain conditions.
- Uncertainty Principle: Proposed by Heisenberg, this principle states that it is impossible to simultaneously know both the position and momentum of a particle with absolute precision. The more precisely one is measured, the less certain the other becomes.
- Schrödinger Equation: This equation describes the state of a quantum system, representing a particle's state over time and space through its wave function.
- Wavefunction Collapse: Before measurement, a particle exists in multiple possible states simultaneously, known as superposition. Upon observation, the wavefunction collapses into a specific state.
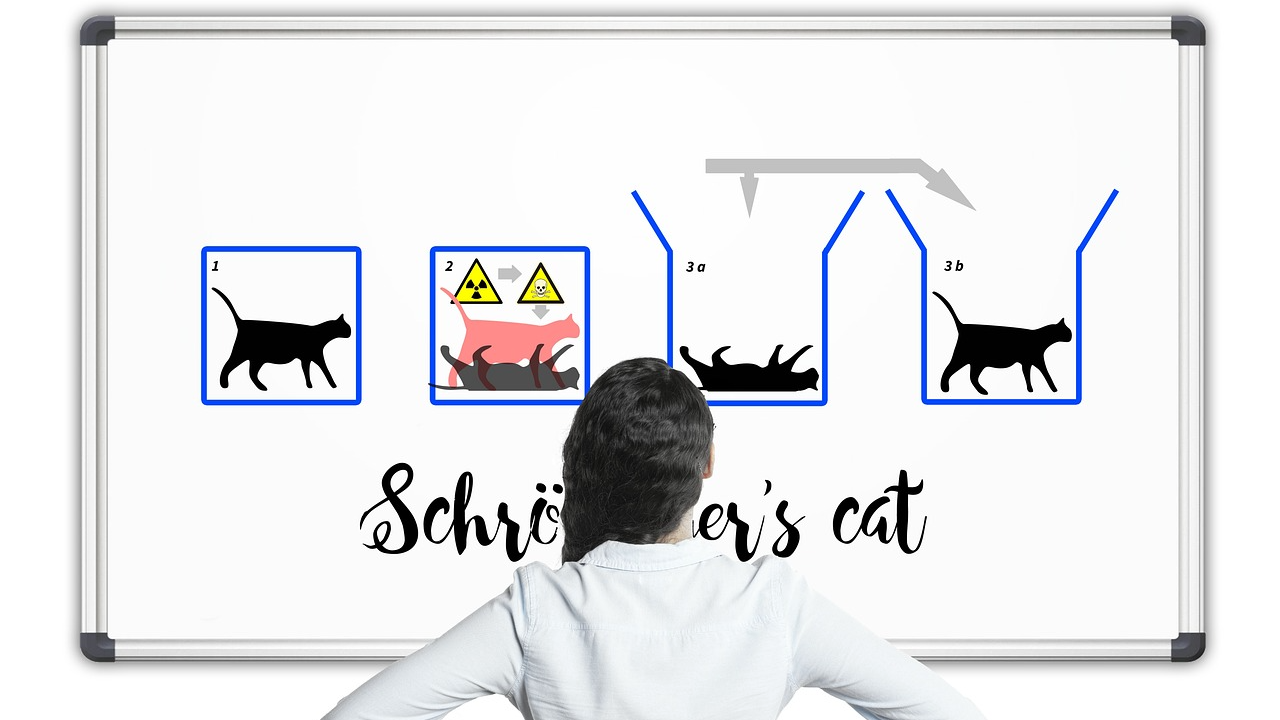
주요 개념과 현상
- 중첩(Superposition): 입자는 동시에 여러 상태에 있을 수 있으며, 파동함수가 이를 기술합니다. 예를 들어, 양자 컴퓨팅에서 큐비트는 0과 1의 상태를 동시에 가질 수 있습니다.
- 얽힘(Entanglement): 두 입자가 얽혀 있는 상태에서는 거리가 아무리 멀어도 서로의 상태가 상호 의존적으로 연결됩니다. 이는 아인슈타인이 '유령 같은 원거리 작용'이라고 표현했던 현상입니다.
- 양자 터널링(Tunneling): 입자가 에너지가 부족함에도 불구하고 잠재적 장벽을 뚫고 지나가는 현상으로, 이는 고전 물리학으로는 설명할 수 없습니다.
Key Concepts and Phenomena
- Superposition: Particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously, described by a wave function. In quantum computing, for instance, qubits can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously.
- Entanglement: When two particles are entangled, their states remain interdependent regardless of the distance between them. Einstein referred to this phenomenon as "spooky action at a distance."
- Quantum Tunneling: A phenomenon where particles pass through potential barriers even when they lack the classical energy required to do so.

양자 역학의 응용 분야
양자 역학은 현대 기술의 핵심을 형성하고 있습니다. 몇 가지 중요한 응용 분야는 다음과 같습니다:
- 양자 컴퓨팅: 큐비트의 중첩과 얽힘을 활용하여 기존 컴퓨터로는 불가능한 연산을 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 레이저와 반도체: 반도체 소자, LED, 태양광 발전 및 레이저 기술은 양자 역학 원리를 기반으로 합니다.
- 의료와 약물 개발: 양자 화학은 분자 수준에서의 상호작용을 이해하고 신약 개발에 중요한 정보를 제공합니다.
Applications of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is foundational to modern technology. Here are some significant applications:
- Quantum Computing: Utilizing the principles of superposition and entanglement, quantum computers can perform computations impossible for classical computers.
- Lasers and Semiconductors: Semiconductor devices, LEDs, solar power technologies, and lasers are based on quantum mechanical principles.
- Medicine and Drug Development: Quantum chemistry helps understand interactions at the molecular level, aiding in the discovery of new drugs.